Tremendous advances have been made in the use of drugs to treat many heart conditions. These drugs can help prevent certain heart conditions from getting worse, prolong life and reduce the effect of symptoms on the ability to perform daily activities.
Drug therapy can:
Lower cholesterol levels
Eliminate chest pain
Help the kidneys eliminate excess water in the blood, thus reducing the volume of blood that the heart has to pump
Lower blood pressure
Make the heart beat more slowly
Open up blood vessels, thus lowering blood pressure
Prevent the blood from creating life-threatening clots
Regulate the heartbeat
While many different drugs may be prescribed, the major categories of drugs used to treat heart conditions are:
ACE Inhibitors
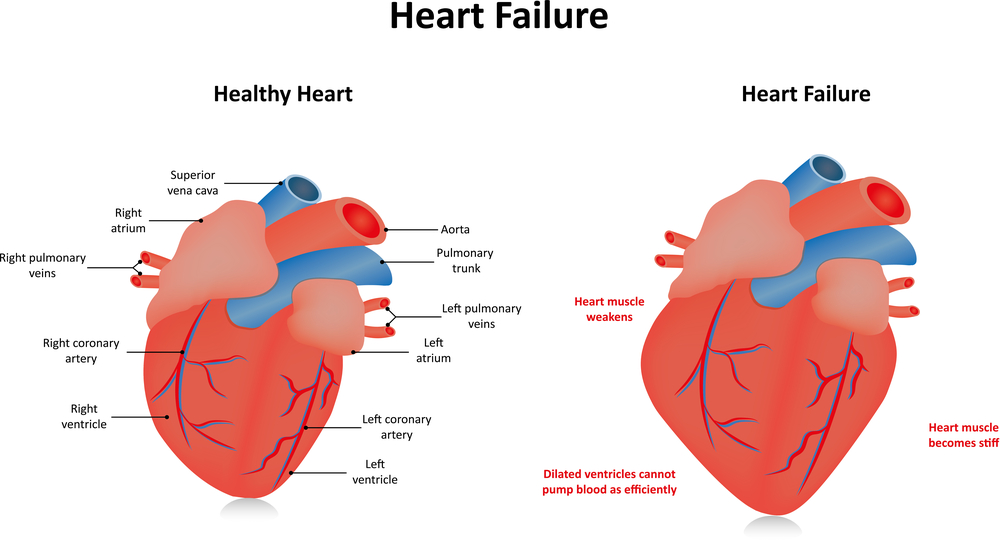 ACE Inhibitors lower the levels of two hormones (angiotensin II and aldosterone) that help increase blood pressure. ACE inhibitors cause arteries and veins to widen and help the kidneys eliminate excess water. Both of these actions lower the blood pressure, allow more oxygen to reach the heart and reduce the amount of work the heart has to do. ACE inhibitors are used to treat congestive heart failure and high blood pressure.
ACE Inhibitors lower the levels of two hormones (angiotensin II and aldosterone) that help increase blood pressure. ACE inhibitors cause arteries and veins to widen and help the kidneys eliminate excess water. Both of these actions lower the blood pressure, allow more oxygen to reach the heart and reduce the amount of work the heart has to do. ACE inhibitors are used to treat congestive heart failure and high blood pressure.
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers
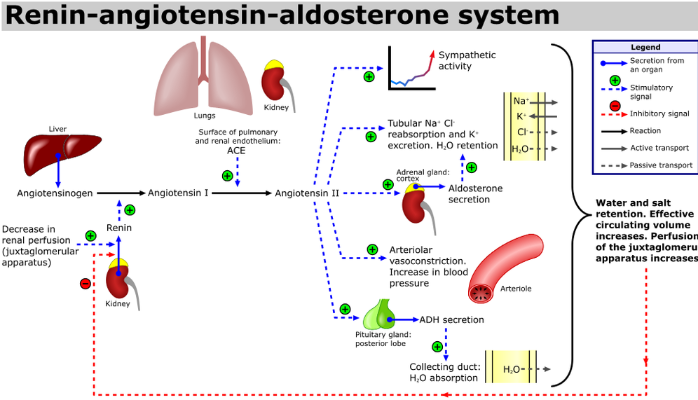 Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers are used to treat high blood pressure. These drugs block the action of an enzyme (angiotensin II) that makes the blood vessels get narrower. They work more directly than ACE inhibitors and may cause fewer side effects. Angiotensin II receptor blockers may be combined with ACE inhibitors but are sometimes used alone in people who cannot take ACE inhibitors.
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers are used to treat high blood pressure. These drugs block the action of an enzyme (angiotensin II) that makes the blood vessels get narrower. They work more directly than ACE inhibitors and may cause fewer side effects. Angiotensin II receptor blockers may be combined with ACE inhibitors but are sometimes used alone in people who cannot take ACE inhibitors.
Antiarrhythmics
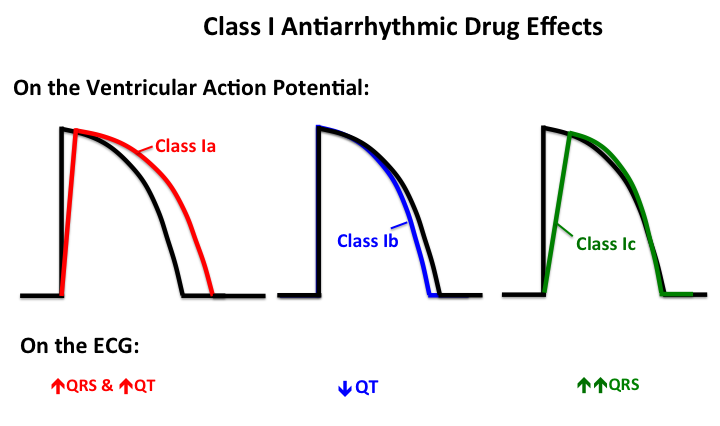 Antiarrhythmics are used to treat disorders of the heart's rhythm, such as arrhythmias or atrial fibrillation. These disorders cause heart palpitations, irregular heartbeats, fast heartbeats, lightheadedness, fainting, chest pain and shortness of breath.
Antiarrhythmics are used to treat disorders of the heart's rhythm, such as arrhythmias or atrial fibrillation. These disorders cause heart palpitations, irregular heartbeats, fast heartbeats, lightheadedness, fainting, chest pain and shortness of breath.
Different types of antiarrhythmics work in different ways. Generally, they slow the electrical impulses in the heart so that the heart can return to a regular rhythm.
Anticoagulants
 Anticoagulants do not actually make the blood thinner. These drugs prevent the blood from forming clots, which can block arteries, veins or the valves of the heart. Common anticoagulants are aspirin, warfarin and heparin.It help reduce the risk for heart attack, stroke and blockages in veins and arteries, such as ones caused by phlebitis. While these types of drugs can prevent a clot from forming, they do not have an impact on a clot that already exists.
Anticoagulants do not actually make the blood thinner. These drugs prevent the blood from forming clots, which can block arteries, veins or the valves of the heart. Common anticoagulants are aspirin, warfarin and heparin.It help reduce the risk for heart attack, stroke and blockages in veins and arteries, such as ones caused by phlebitis. While these types of drugs can prevent a clot from forming, they do not have an impact on a clot that already exists.
Beta Blockers
 Beta Blockers block the effect of adrenaline (the hormone norepinephrine) on the body's beta receptors. This slows down the nerve impulses that travel through the heart. As a result, the resting heart rate is lower, the heart does not have to work as hard and the heart requires less blood and oxygen. Beta blockers can also block the impulses that can cause an arrhythmia. Alcohol should also be avoided because it can decrease the effects of the beta blockers.
Beta Blockers block the effect of adrenaline (the hormone norepinephrine) on the body's beta receptors. This slows down the nerve impulses that travel through the heart. As a result, the resting heart rate is lower, the heart does not have to work as hard and the heart requires less blood and oxygen. Beta blockers can also block the impulses that can cause an arrhythmia. Alcohol should also be avoided because it can decrease the effects of the beta blockers.
Calcium-Channel Blockers
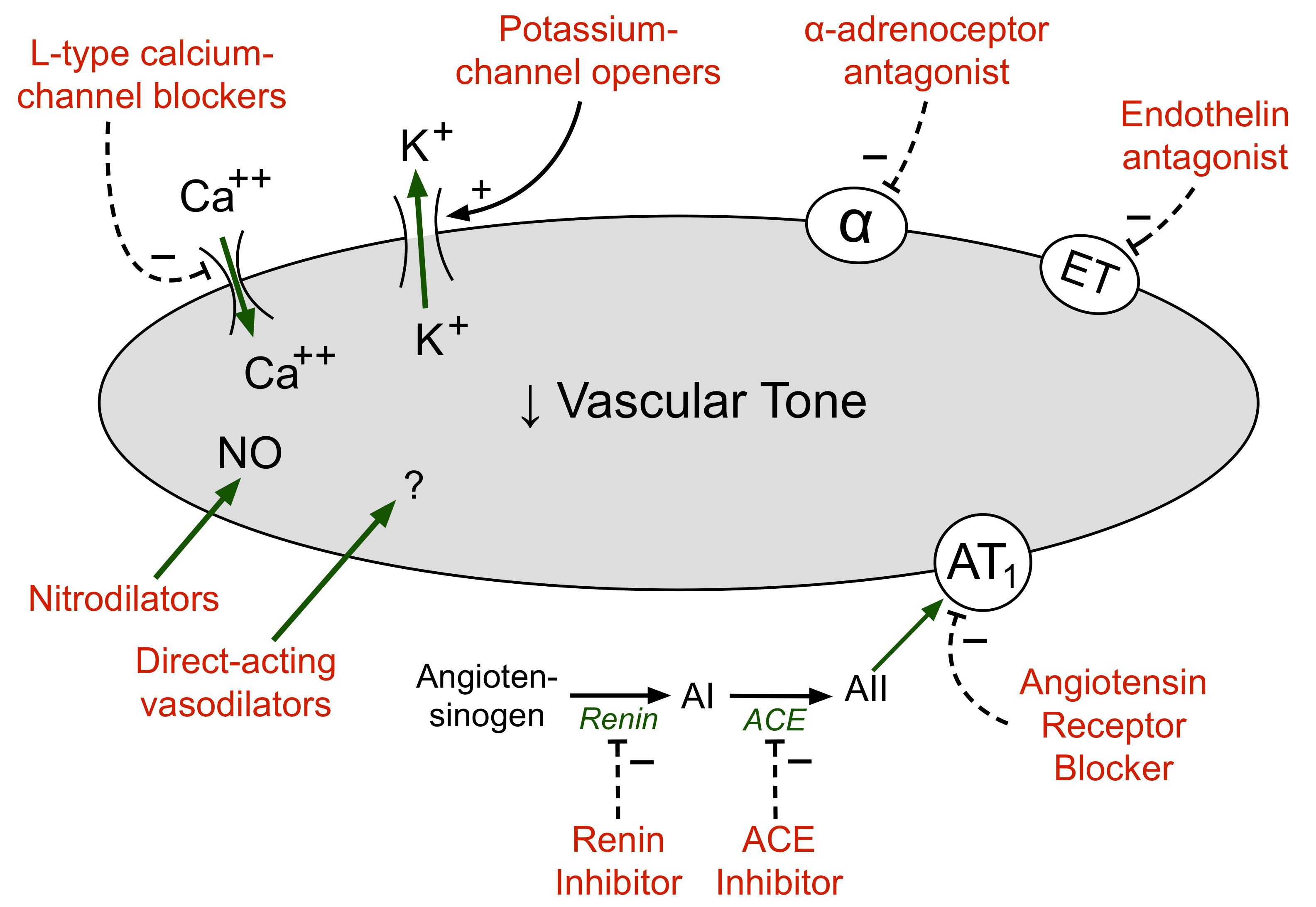 Calcium-Channel Blockers cause the blood vessels to relax by slowing the rate at which calcium passes into the heart muscle and blood vessel walls. As the blood vessels relax, more blood can flow through them, lowering the blood pressure. Calcium-channel blockers are prescribed to manage high blood pressure, chest pain (angina) or irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia).Patients should avoid smoking, which may cause a rapid heartbeat (tachycardia).
Calcium-Channel Blockers cause the blood vessels to relax by slowing the rate at which calcium passes into the heart muscle and blood vessel walls. As the blood vessels relax, more blood can flow through them, lowering the blood pressure. Calcium-channel blockers are prescribed to manage high blood pressure, chest pain (angina) or irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia).Patients should avoid smoking, which may cause a rapid heartbeat (tachycardia).
Cholesterol-Lowering Medicines
 If cholesterol levels cannot be brought down to healthy levels by diet and exercise, cholesterol-lowering drugs may be helpful. They are also prescribed for people who have inherited a medical condition that causes high cholesterol.
If cholesterol levels cannot be brought down to healthy levels by diet and exercise, cholesterol-lowering drugs may be helpful. They are also prescribed for people who have inherited a medical condition that causes high cholesterol.
Patients should avoid drinking and taking statins until they have talked about it with the doctor.
Digitalis
 Digitalis increases the force of each heartbeat by increasing the amount of calcium in the heart's cells. It can control irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) by slowing the signals that start in the sinoatrial node, which reduces the number of signals that travel through the atrioventricular node and reduces irregular heartbeats. Digitalis increases blood flow throughout the body and can reduce swelling in the hands and ankles caused by blood pooling.
Digitalis increases the force of each heartbeat by increasing the amount of calcium in the heart's cells. It can control irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) by slowing the signals that start in the sinoatrial node, which reduces the number of signals that travel through the atrioventricular node and reduces irregular heartbeats. Digitalis increases blood flow throughout the body and can reduce swelling in the hands and ankles caused by blood pooling.
Diuretics
 Diuretics reduce the amount of salt and water in the body. As the kidneys filter the excess water from the blood, the volume of blood the heart has to pump is reduced, causing blood pressure to go down. Diuretics are given when the have congestive high blood pressure, swelling or water retention (edema) or heart failure. They may also be prescribed for certain kinds of kidney or liver disease.
Diuretics reduce the amount of salt and water in the body. As the kidneys filter the excess water from the blood, the volume of blood the heart has to pump is reduced, causing blood pressure to go down. Diuretics are given when the have congestive high blood pressure, swelling or water retention (edema) or heart failure. They may also be prescribed for certain kinds of kidney or liver disease.
Nitrates
 Nitrates are used to treat chest pain associated with angina and to reduce the symptoms of congestive heart failure. They are called vasodilators because they cause the blood vessels to widen. This makes the blood flow better, reduces blood pressure, reduces the workload on the heart and allows more oxygen-rich blood to reach the heart muscle. Patients should avoid smoking when taking nitrates. Smoking can decrease the effect of the medicine.
Nitrates are used to treat chest pain associated with angina and to reduce the symptoms of congestive heart failure. They are called vasodilators because they cause the blood vessels to widen. This makes the blood flow better, reduces blood pressure, reduces the workload on the heart and allows more oxygen-rich blood to reach the heart muscle. Patients should avoid smoking when taking nitrates. Smoking can decrease the effect of the medicine.
