 We offer the spectrum of clinical cardiac services, ranging from preventative services to Radionuclide Angiography.
We offer the spectrum of clinical cardiac services, ranging from preventative services to Radionuclide Angiography.
At the core of each clinical subsection is a devotion to optimizing patient outcomes by bringing highly trained staff, state-of-the-art technology, and cutting edge techniques to the patient suffering from cardiovascular disease.
Some of our Cardiac Services include the following:
Treadmill stress test
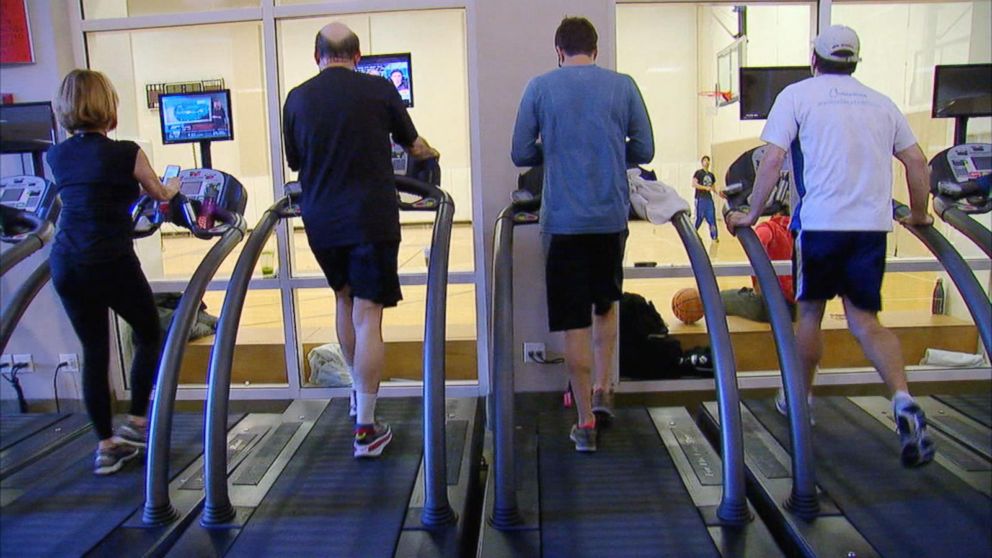

As long as you can walk and have a normal ECG, this is normally the first stress test performed. You walk on a treadmill while being monitored to see how far you walk and if you develop chest pain or changes in your ECG that suggest that your heart is not getting enough blood.
Dobutamine or Adenosine Stress Test
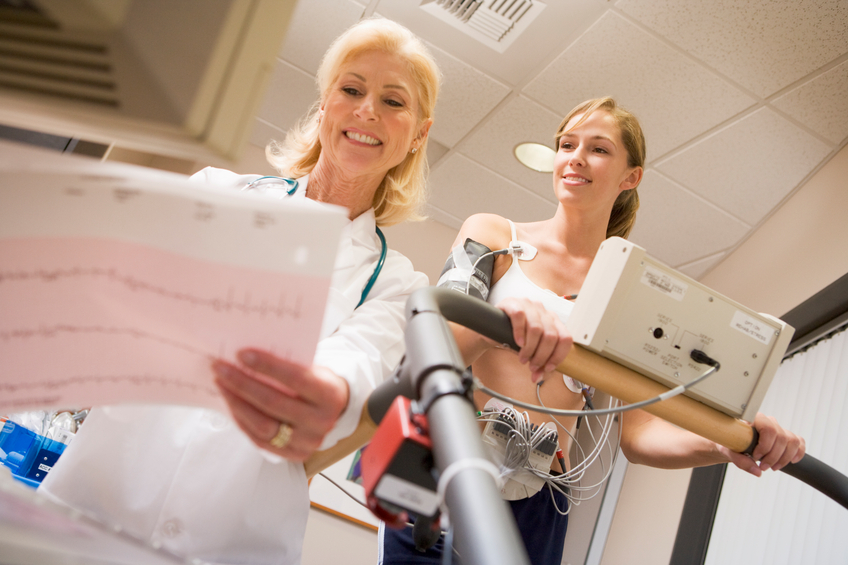 This test is used in people who are unable to exercise. A drug is given to make the heart respond as if the person were exercising. This way the doctor can still determine how the heart responds to stress, but no exercise is required.
This test is used in people who are unable to exercise. A drug is given to make the heart respond as if the person were exercising. This way the doctor can still determine how the heart responds to stress, but no exercise is required.
Nuclear stress test
 This test helps to determine which parts of the heart are healthy and function normally and which are not. A small amount of radioactive substance is injected into the patient. Then the doctor uses a special camera to identify the rays emitted from the substance within the body; this produces clear pictures of the heart tissue on a monitor. These pictures are done both at rest and after exercise. Using this technique, areas of the heart that have a decreased blood supply can be detected.
This test helps to determine which parts of the heart are healthy and function normally and which are not. A small amount of radioactive substance is injected into the patient. Then the doctor uses a special camera to identify the rays emitted from the substance within the body; this produces clear pictures of the heart tissue on a monitor. These pictures are done both at rest and after exercise. Using this technique, areas of the heart that have a decreased blood supply can be detected.
Echocardiogram
 An echocardiogram (also called an echo) is a type of ultrasound test that uses high-pitched sound waves that are sent through a device called a transducer. The device picks up echoes of the sound waves as they bounce off the different parts of your heart. These echoes are turned into moving pictures of your heart that can be seen on a video screen.
An echocardiogram (also called an echo) is a type of ultrasound test that uses high-pitched sound waves that are sent through a device called a transducer. The device picks up echoes of the sound waves as they bounce off the different parts of your heart. These echoes are turned into moving pictures of your heart that can be seen on a video screen.
Stress echocardiogram
 An echocardiogram (often called "echo") is a graphic outline of the heart's movement. A stress echo can accurately visualize the motion of the heart's walls and pumping action when the heart is stressed; it may reveal a lack of blood flow that isn't always apparent on other heart tests.
An echocardiogram (often called "echo") is a graphic outline of the heart's movement. A stress echo can accurately visualize the motion of the heart's walls and pumping action when the heart is stressed; it may reveal a lack of blood flow that isn't always apparent on other heart tests.
Doppler echocardiogram
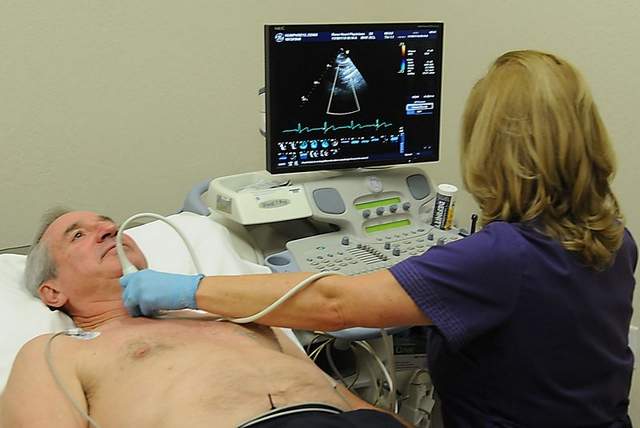 This test is used to look at how blood flows through the heart chambers, heart valves, and blood vessels. The movement of the blood reflects sound waves to a transducer. The ultrasound computer then measures the direction and speed of the blood flowing through your heart and blood vessels. Doppler measurements may be displayed in black and white or in color.
This test is used to look at how blood flows through the heart chambers, heart valves, and blood vessels. The movement of the blood reflects sound waves to a transducer. The ultrasound computer then measures the direction and speed of the blood flowing through your heart and blood vessels. Doppler measurements may be displayed in black and white or in color.
24 Hour Holter Monitor
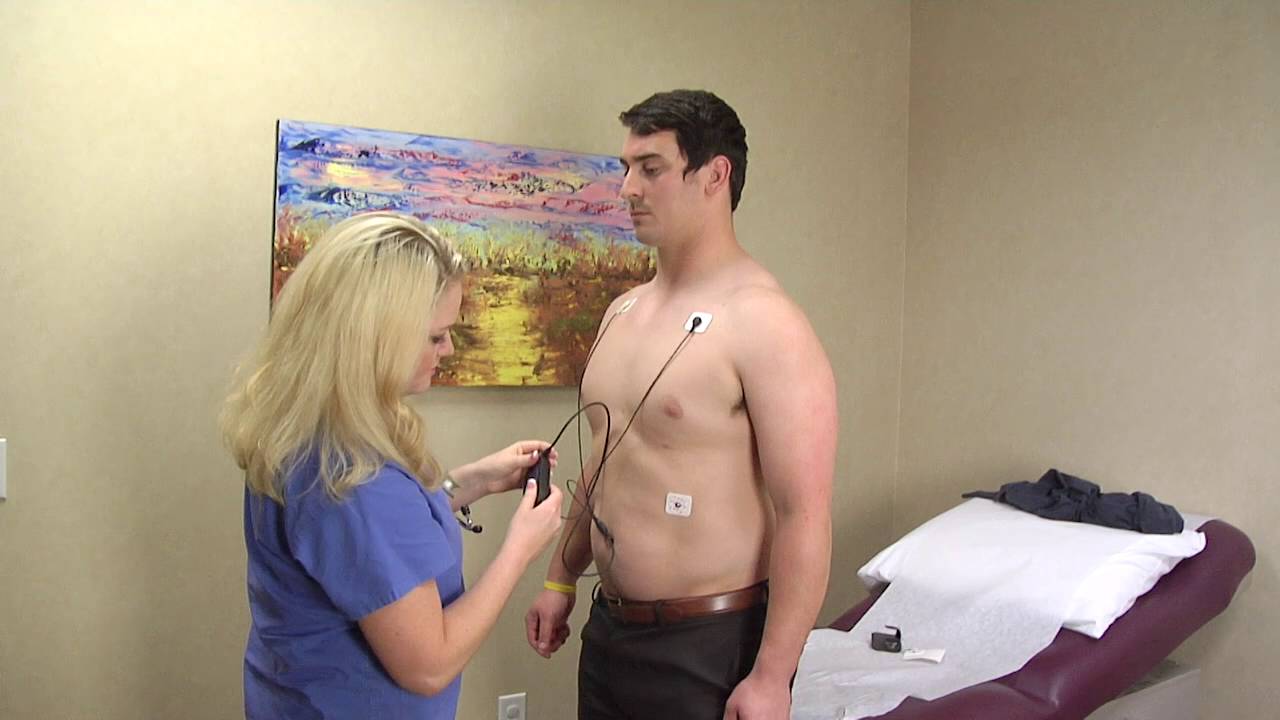 A Holter monitor is a battery-operated portable device that measures and tape records your heart’s activity (ECG) continuously for 24 hours or longer depending on the monitor used. The device is the size of a small camera. It has wires with silver dollar-sized electrodes that attach to your skin. The Holter monitor and other devices that record your ECG as you go about your daily activities are called ambulatory electrocardiograms.
A Holter monitor is a battery-operated portable device that measures and tape records your heart’s activity (ECG) continuously for 24 hours or longer depending on the monitor used. The device is the size of a small camera. It has wires with silver dollar-sized electrodes that attach to your skin. The Holter monitor and other devices that record your ECG as you go about your daily activities are called ambulatory electrocardiograms.
Cardiac event recorder
 A cardiac event recorder is a battery-powered portable device that you control to tape-record your heart’s electrical activity (ECG) when you have symptoms. There are two types of event recorders: a loop memory monitor and a symptom event monitor.
A cardiac event recorder is a battery-powered portable device that you control to tape-record your heart’s electrical activity (ECG) when you have symptoms. There are two types of event recorders: a loop memory monitor and a symptom event monitor.
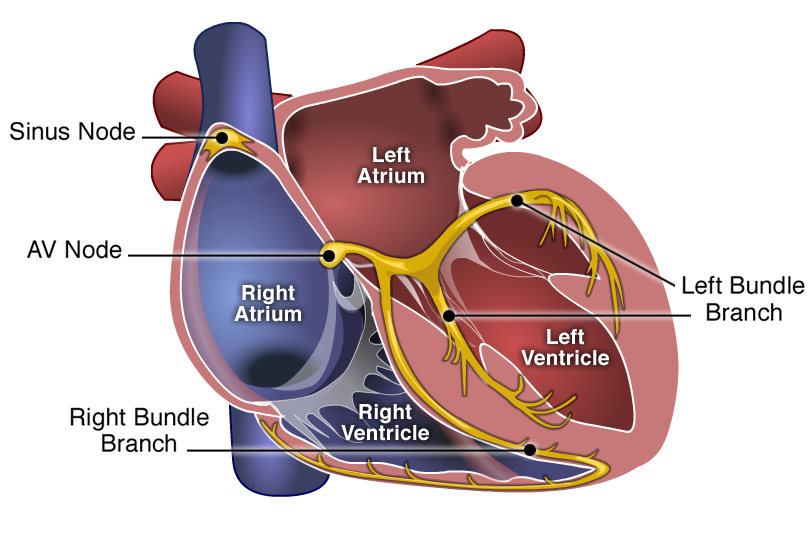
ECG
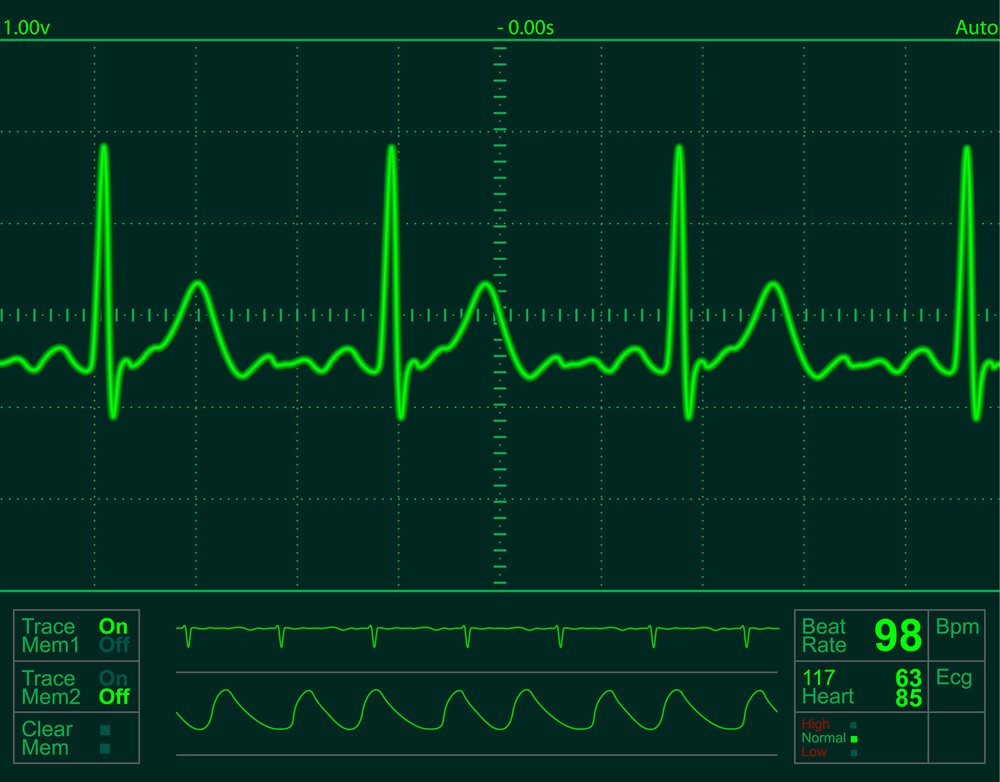 An electrocardiogram — abbreviated as ECG or EKG — is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart. A normal heartbeat on ECG will show the timing of the top and lower chambers.
An electrocardiogram — abbreviated as ECG or EKG — is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart. A normal heartbeat on ECG will show the timing of the top and lower chambers.
The right and left atria or upper chambers make the first wave called a “P wave" — following a flat line when the electrical impulse goes to the bottom chambers. The right and left bottom chambers or ventricles make the next wave called a “QRS complex." The final wave or “T wave” represents electrical recovery or return to a resting state for the ventricles.
Cardiac catheterization
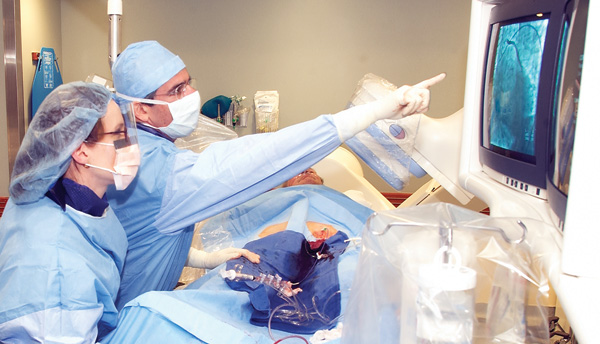 Cardiac catheterization (cardiac cath or heart cath) is a procedure to examine how well your heart is working. A thin, hollow tube called a catheter is inserted into a large blood vessel that leads to your heart.
Cardiac catheterization (cardiac cath or heart cath) is a procedure to examine how well your heart is working. A thin, hollow tube called a catheter is inserted into a large blood vessel that leads to your heart.
Angioplasty
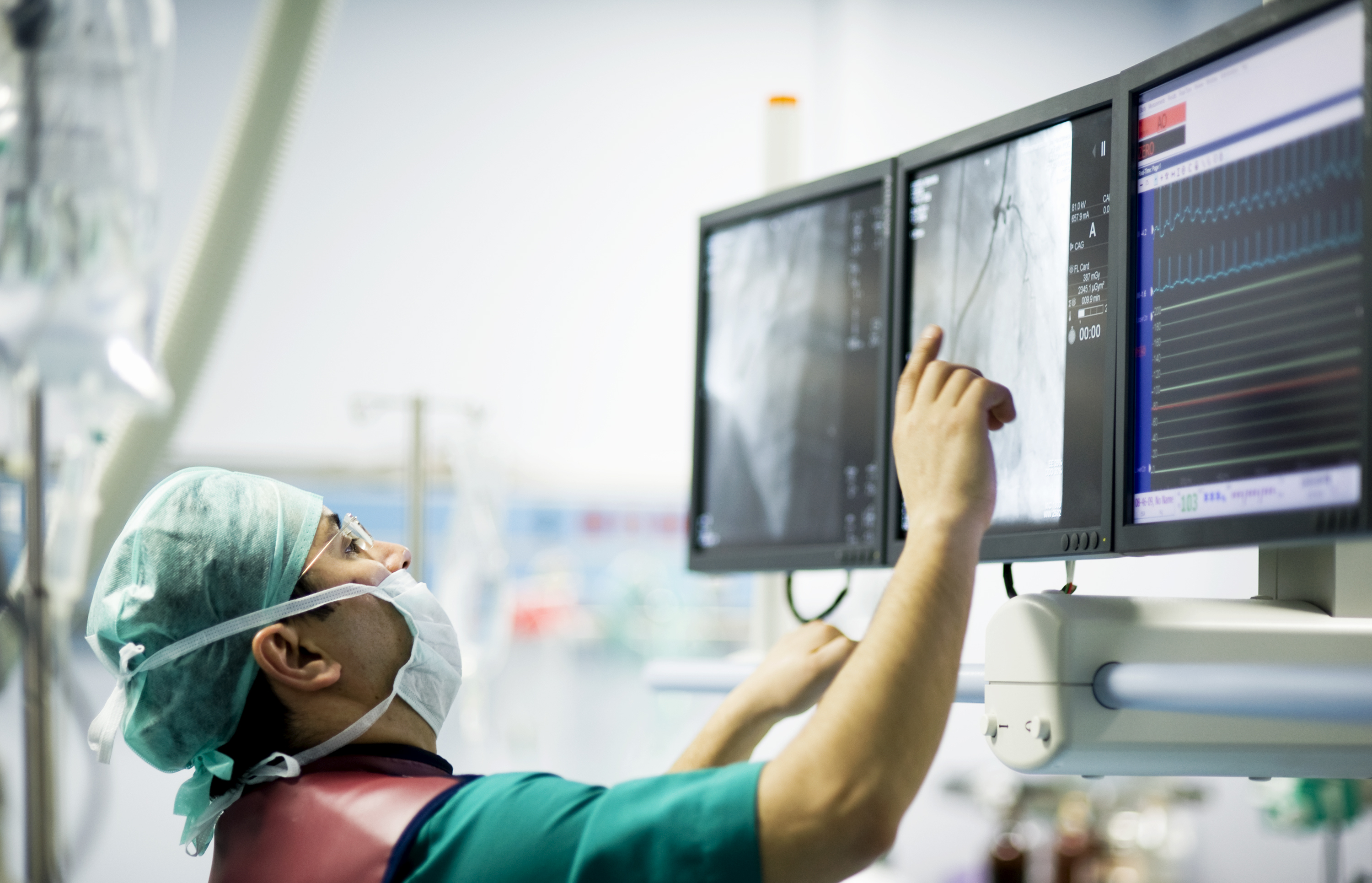
Angioplasty, also known as percutaneous intervention, is a procedure in which a thin tube called a catheter is threaded into the heart with a deflated balloon at the tip. The balloon is then inflated to open spots where blood flow has been reduced or blocked. While doing an angioplasty, doctors may also implant a mesh tube called a stent to help prop open the artery, reducing the chance of another blockage. Another type of angioplasty is a laser angioplasty; instead of a balloon, the catheter carries a laser tip that sends pulsating beams of light to clear blockages.
Stent
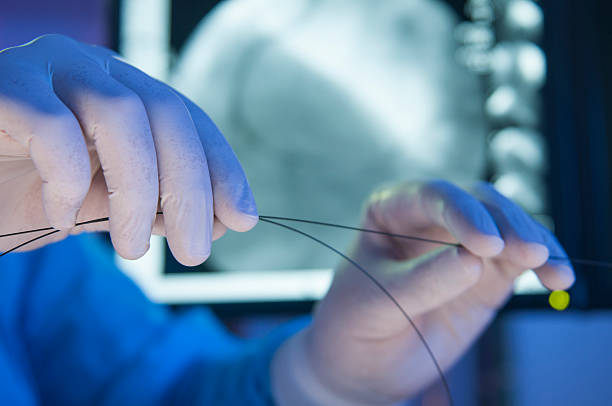 A stent is a wire mesh tube that's inserted into a narrowed coronary artery to prop it open, prevent re-blockage and allow the heart muscle to get the blood flow and oxygen it needs. A stent can also be placed in narrowed carotid arteries (the vessels in the front of the neck that supply blood to the brain) to treat patients at high risk for stroke.
A stent is a wire mesh tube that's inserted into a narrowed coronary artery to prop it open, prevent re-blockage and allow the heart muscle to get the blood flow and oxygen it needs. A stent can also be placed in narrowed carotid arteries (the vessels in the front of the neck that supply blood to the brain) to treat patients at high risk for stroke.
Permanent pacemakers
 An artificial pacemaker is an electrical device implanted to keep a heart beating at the right speed and rhythm. It is needed when a person’s natural pacemaker either doesn’t work properly or the impulse is not transmitted adequately to the ventricles for the heart to contract. Pacemakers are typically used for hearts that beat too slowly or irregularly.
An artificial pacemaker is an electrical device implanted to keep a heart beating at the right speed and rhythm. It is needed when a person’s natural pacemaker either doesn’t work properly or the impulse is not transmitted adequately to the ventricles for the heart to contract. Pacemakers are typically used for hearts that beat too slowly or irregularly.
